BUNSEKI KAGAKU, Abstracts
Vol. 4 9, No. 9
September, 2000
Review
Toyohide Takeuchi*
*Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Engineering, Gifu University, Gifu 501-1193
(Received 4 April 2000)
When appropriate detection methods are not available, indirect detection can be a candidate in ion chromatography, reversed-phase liquid chromatography and ion-pair chromatography. Indirect detection is classified according to the type of interaction between the analytes and the visualization agents. Analytes are usually visualized in indirect detection via ion exchange or an interaction with a mobile-phase additive in the column. A post-column ion replacement or enzyme reaction generates detectable species and visualizes analytes. Analytes can be visualized even if such interactions are not involved when the dynamic reserve, defined as the ratio of the background to its noise level, is sufficiently high. The detection principles of these methods are described in this article.
Keywords : liquid chromatography; ion chromatography; indirect detection; visualization; detection principle.
Research Papers
Kenji Fujiwara* and Taketoshi Nakahara**
*Lighting Development Center, Lighting Company, Matsushita Electronics Corporation, 1-1, Saiwai-cho, Takatsuki-shi, Osaka 569-1193
**Department of Applied Chemistry, Graduate school of Engineering, Osaka Prefecture University, 1-1, Gakuen-cho, Sakai-shi, Osaka 599-8531
(Received 1 March 2000, Accepted 22 May 2000)
With respect to recent environmental pollution, it is required in the lighting industry to reduce the amount of mercury(Hg) enclosed within fluorescent lamps. So far, various chemical and physical analytical techniques have provided great results in solving the behavior of Hg in a fluorescent lamp. Upon determining Hg in a fluorescent lamp, a chemical analysis with a wet digestion procedure causes a possibility of vaporization of Hg during the pretreatment step, a limitation of the analysis in a specific part of the fluorescent lamp, and difficulties in conducting rapid analysis. Therefore, we developed a rapid and simple semi-quantitative determination of Hg in a specific part of the fluorescent lamp by laser ablation(LA)/ICP-MS. Regarding the calibration method, using europium(Eu) as an internal element, which is about 2 wt% of the content of phosphor used in the fluorescent lamp, the ratio of the Hg/Eu intensity was determined, and the relative sensitivity factor(RSF) of the Hg/Eu intensity was determined by using a pellet made of cellulose powder mixed with europium oxide and mercury oxide, and the amount of Hg in the fluorescent lamp could be calculated from the Hg/Eu of phosphor and the RSF value. The relative standard deviation for 5 replicate measurements of 60 µg g-1 Hg was less than 20%. The detection limit(3σ) was 3.6 µg g-1. We confirmed that this technique could be a rapid and simple semi-quantitative analysis of Hg in a specific part of the fluorescent lamp without any wet pretreatment.
Keywords : mercury; fluorescent lamp; phosphor; laser ablation/ICP-MS; relative sensitivity factor.
Toshio Ogawa, Takao Sonogashira and Satoshi Osawa*
*Laboratory for Materials Design Engineering, Kanazawa Institute of Technology, 7-1, Ohgigaoka, Nonoichi, Ishikawa 921-8501
(Received 16 February 2000, Accepted 28 May 2000)
A method for estimating the wavenumber of a sulfonyl group in the infrared absorption spectra of organic compounds is discussed. This estimation is achieved by taking into account the additive properties in the effect of adjacent groups, i.e., the group shift, and using a method of multiple-regression analysis. The accuracy of the values was improved by classifying the compounds depending upon the existing states. Especially, the results in vapor and liquid states were excellent. The wavenumbers were generally predicted by ν(cm-1)=a+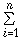 βiXi, where βi is the value of the group-shift and Xi the number for the adjacent group of i-th type; a is a constant. These values change depending upon the state, such as vapor or liquid. Thus, we developed a method in which the peak positions of a sulfonyl group can be predicted from the value of a group shift of the adjacent groups.
βiXi, where βi is the value of the group-shift and Xi the number for the adjacent group of i-th type; a is a constant. These values change depending upon the state, such as vapor or liquid. Thus, we developed a method in which the peak positions of a sulfonyl group can be predicted from the value of a group shift of the adjacent groups.
Keywords : multiple-regression analysis; sulfonyl group; infrared spectra; adjacent functional group.
Tadao Sakai, Norio Teshima, Maho Kayukawa and Satomi Sawamura*
*Department of Applied Chemistry, Aichi Institute of Technology, 1247, Yachigusa, Yakusa-cho, Toyota-shi, Aichi 470-0392
(Received 1 March 2000, Accepted 9 June 2000)
A sensitive spectrophotmetric method for the determination of phenol using a solid-phase extraction cartridge was developed. It is based on the oxidative coupling of 4-aminoantipyrine with phenol to form an azo compound (aminoantipyrine dye) in the presence of hexacyanoferrate(III) at pH 10. The formed azo compound was adsorbed on a Sep-Pak C18 cartridge. After the concentrated compound was eluted with a 60%(v/v) acetonitrile solution, the absorbance was measured at 503 nm. On the other hand, a sample solution containing phenol was passed directly through a Porapak RDX cartridge, and was then eluted with a 90%(v/v) methanol solution. The elute was measured at 501 nm after adding reagents and developing the color intensity. The proposed methods using Sep-Pak C18 and Porapak RDX cartridges showed a high enhancement factor (10~100) and made it possible to determine the 1~8 ng ml-1 level of phenol with a low relative standard deviation. The recoveries of 1 and 4 ng ml-1 phenol added to tap water were 96 and 95% for Sep-Pak C18 and those of 2 and 4 ng ml-1 were 103 and 88% for Porapak RDX.
Keywords : solid-phase extraction; trace phenol determination; tap water; 4-aminoantipyrine method.
Naoki Yamaguchi, Yukiko Okada, Shogo Suzuki, Shoji Hirai* and Toshiaki Mitsugashira**
*Faculty of Engineering, Musashi Institute of Technology, 1-28-1, Tamatsutsumi, Setagaya-ku, Tokyo 158-8557
**The Oarai branch, Institute for Materials Reserch, Tohoku University, Narita-cho, Oarai-machi, Higashiibaraki- gun, Ibaraki 311-1313
(Received 10 March 2000, Accepted 14 June 2000)
A new radiochemical procedure was applied to the isolation of activated cobalt (58Co and 60Co) in high-purity iron irradiated by reactor neutrons. After irradiation, the sample was dissolved in a 8 M HCl solution and the activated cobalt in 5 M HCl was isolated removing 59Fe, 54Mn and 51Cr by anion-exchange chromatography. CoCl2 powder was added into the activated cobalt fraction and Co(OH)2 was precipitated by adding excess 8 M NaOH solution. Finally, the precipitates were mounted for gamma-ray spectrometry. The overall recovery of activated cobalt was 99%. The decontamination factor of 59Fe was 2×104. The procedure was successfully applied to the determination of a ppb-level of nickel and cobalt in high-purity iron irradiated by epi-thermal neutrons of the Japan Materials Testing Reactor of JAERI.
Keywords : radiochemical neutron activation analysis; ppb amount of nickel and cobalt in high-purity iron; anion-exchange chromatography; precipitation with Co(OH)2.
Kunihiro Watanabe, Hisashi Isomura and Masayuki Itagaki*
*Department of Industrial Chemistry, Faculty of Science and Technology, Science University of Tokyo, 2641, Yamazaki, Noda-shi, Chiba 278-8510
(Received 5 April 2000, Accepted 16 June 2000)
A separation method between Tl(I) and Tl(III) in the presence of other heavy metals has been developed under pseudo three-phase equilibrium. Filter-paper phase separators were used to separate the aqueous phase from a mixture of organic solvent and water under high-speed stirring. First, Tl(I), Tl(III) and other heavy metals were added to the aqueous phases in vessels A and B, respectively. Thiooxine-CHCl3 solvent was added to extraction vessel A to extract Tl(I), and 1-(2-pyridylazo)-2-naphthol(PAN)-CHCl3 solvent was added to extraction vessel B to extract Tl(III). EDTA as masking agent was added to each vessel to suppress the extraction of heavy metals. After 80 minutes of extraction under high-speed stirring, Tl(I) was extracted above 99% into the thiooxine-CHCl3 phase, and Tl(III) was extracted above 99% into the PAN-CHCl3 phase. Also, Mn(II), Fe(III), Ni(II) ,Cu(II), and Zn(II) as heavy metals remained in the aqueous phase by masking with EDTA. Tl(I) and Tl(III) could be separated up to 1000 µg and 1100 µg in the presence of other metals, respectively. The separation of Tl(I) and Tl(III) was achieved by the differences between the distribution constants of thiooxine and PAN-Tl complexs in the each vessel.
Keywords : pseudo three-phase equilibrium; solvent extraction; thallium(I); thallium(III).
Kunihiro Watanabe, Kazue Yamaguchi and Masayuki Itagaki*
*Department of Industrial Chemistry, Faculty of Science and Technology, Science University of Tokyo, 2641, Yamazaki, Noda-shi, Chiba 278-8510
(Received 22 March 2000, Accepted 20 June 2000)
To improve the analytical sensitivity, the tridentate ligand azo-compounds derivatives of 1-amino-8-hydroxy-7-(o-hydroxyphenylazo)-3,6-naphthalenedisulfonic acid(7-o-OH) were synthesized, and the effect of substituted groups on the sensitivity was investigated by making a comparison of their color-fading rate. The fading rate of azo-compound increased along with a decrease in the Hammett constant (σ) and an increase in pKa; this was accelerated by substituting electron-donative groups to the compounds. Azo-compounds having electron-donative groups were useful as sensitive reagents for catalytic analysis. The optimum conditions for determining Mn(II) were investigated using the most sensitive reagent, 1-amino-8-hydroxy-7-(o-hydroxy-p-metylphenylazo)-3,6-naphthalenedisulfonic acid (p-CH3), among the examined azo-compounds. A calibration curve was made between ln(A1/A5) and the concentration of Mn(II) under the optimum conditions: 3.0×10-5 M p-CH3, 1.5×10-3 M 1,10-phenanthroline, 1.1×10-1 M H2O2, pH 10.3, 30°C. The value of ln(A1/A5) was nearly proportional up to 4 ppb of Mn(II). The detection limit of Mn(II) was 6 ppt.
Keywords : effect of substituted groups; tridentate ligand azo-compounds; catalytic analysis; 1-amino-8-hydroxy-7-(o-hydroxy-p-metylphenylazo)-3,6-naphthalenedisulfonic acid.
Technical Papers
Mitsuyoshi Watanabe and Akira Narukawa*
*Material Research Laboratory, Corporate R&D Group, NGK Insulators, Ltd., 2-56, Suda-cho, Mizuho-ku, Nagoya 467-8530
(Received 24 April 2000, Accepted 12 June 2000)
Determining the total oxygen content viz. the manganese valence in sintered lanthanum manganites, La1-X(Ca,Sr)XMnO3+Z, is described. In the proposed method, a powdered sample taken in a quartz crucible was dissolved in (1+1) sulfuric acid containing sodium oxalate using a sealed vessel at 40°C, followed by permanganate titration of a excess oxalate. The present method is highly reproducible, requiring a 25 h/sample. A quartz crucible was recommended for sample dissolution, and was inserted in a seald vessel.
Keywords : lanthanum manganites; oxygen content; manganese valence; sealed vessel.
Notes
Tsutomu Shoji, Yuetsu Danzaki, Tetsuya Ashino, Hideyuki Konno and Kan-ichi Makabe*
*Institute for Materials Research, Tohoku University, 2-1-1, Katahira, Aoba-ku, Sendai 980-8577
(Received 1 May 2000, Accepted 29 June 2000)
In determining the constituent elements of various alloys by ICP-OES, complete dissolution of the samples is indispensable. It is effective to use a dissolvent containing complexing agents to dissolve samples in which the constituent elements are easily hydrolyzed, because the hydrolysis of antimony and tin could be prevented by using a HNO3-HCl mixture containing tartaric acid in these elements. By a dissolution method using a HNO3-HCl mixture containing tartaric acid, the constituent elements in antimony and tin alloys could be exactly determined without the hydrolysis of analytical elements. Furthermore, when a mixed dissolvent of 35 ml of HNO3 (diluted 1+1), 5 ml of HCl (diluted 1+1) and 1 g of tartaric acid was used, metallic germanium could be completely dissolved without volatilization as the chloride.
Keywords : dissolution with nitric-hydrochloric-tartaric acids; Sb alloy; Sn alloy; volatilization of Ge; ICP-OES.
Digest of Doctoral Dissertation
Zilin Chen
Department of Applied Chemistry, Graduate School of Engineering, Tokyo Metropolitan University, 1-1, Minami-Ohsawa, Hachiohji, Tokyo 192-0397
(Awarded by Tokyo Metropolitan University dated on March 25, 2000)
The present research focused on the development of ligand exchange-micellar electrokinetic capillary chromatography (LE-MEKC). In this study, a novel chial separation mode, LE-MEKC, was proposed and successfully used in (1) the simultaneous separations of o-, m-, and p-enantiomers of phenylalanine family and positional and optical isomers of tryptophan family; (2) an explanation of the reversal behaviors of enantiomer migration order (EMO); (3) an on-capillary determination of critical micelle concentration of anionic surfactants; (4) an estimation of the formation constants of Cu(II) complexes with mixed amino acid enantiomers; and (5) the enantiomeric separation of hydroxy acids and dipeptides. Further, to reveal the separation mechanism and to provide support evidence for the proposed model, the following aspects were investigated: (1) the dependence of the EMO on the ligand chirality, ligand stereo-conformation and the micelle formation of anionic and cationic surfactants; (2) the relationship between the EMO and ternary complex stability; (3) the influence of the chemical structure and hydrophobicity of the analytes on the resolution and EMO; (3) the relationship between enantioseparation and complexes composition; (4) the partition of solutes (amino acid enantiomers) between the micellar phase and the bulk electrolyte; (5) the effect of organic modifiers on the separation behaviors. The obtained results agreed well with the proposed model.
(Received June 27, 2000)
Keywords : ligand exchange; micellar electrokinetic chromatography; chiral separation; amino acid enantiomer; positional isomer; complex formation constant; critical micelle concentration; enantiomer migration order; hydroxy acid; dipeptide.
Akio Hashimoto
Analytical Chemistry Department, Product & Technology Development Laboratory, Tanabe Seiyaku Co., Ltd., 3-16-89, Kashima, Yodogawa-ku, Osaka 532-8505
(Awarded by Kyoto Pharmaceutical University, dated March 21 ,2000)
A quality evaluation of animal natural medicines, such as Lumbricus and Cervi Parvum Cornu as well as their preparations was conducted. The contents of common constituents (amino acids, nucleic acid components and organic acids) in 11 animal natural medicines were determined using HPLC for the evaluation of each natural medicine. The results showed that the total amino acids content and the nucleic acids components content were characteristic in several particular natural medicines. However, the content of free amino acids, free nucleic acid components and organic acids differed, even in the same animal natural medicine from the same place of production. An analytical DNA technique was also applied to identify animal natural medicines, mainly about Cervi Parvum Cornu. After confirming the presence of DNA in the samples through histrogical examinations, DNA fragments of 12S rRNA and/or cytochrome b gene regions in mtDNA were amplified using the PCR method. Their sequences were then determined by the usual method. It was confirmed that the amplified fragments originated from the DNA of those origins and could be used for the identification of each animal natural medicine. Finally, physico-chemical evaluation methods using the HPLC and PCR mentioned above were applied to identify Lumbricus and Cervi Parvum Cornu in some commercial preparations. It was confirmed that Lumbricus was contained in the preparations through an analysis of common constituents(lombricine and inosine). Cervi Parvum Cornu was identified by a DNA analysis.
(Received July 17, 2000)
Keywords : animal natural medicines; amino acids; nucleic acid components; organic acids; HPLC; DNA; PCR; identification.
Copyright (c) The Japan Society for Analytical Chemistry
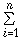 βiXi, where βi is the value of the group-shift and Xi the number for the adjacent group of i-th type; a is a constant. These values change depending upon the state, such as vapor or liquid. Thus, we developed a method in which the peak positions of a sulfonyl group can be predicted from the value of a group shift of the adjacent groups.
βiXi, where βi is the value of the group-shift and Xi the number for the adjacent group of i-th type; a is a constant. These values change depending upon the state, such as vapor or liquid. Thus, we developed a method in which the peak positions of a sulfonyl group can be predicted from the value of a group shift of the adjacent groups.